Bronchiolitis: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention Explained
Bronchiolitis is a common respiratory illness that mostly affects infants and young children, especially during colder months. It occurs when tiny airways in the lungs become inflamed and filled with mucus, making breathing difficult. This condition often starts like a mild cold but can quickly become serious if not treated properly, which is why understanding Bronchiolitis and its warning signs is extremely important for parents and caregivers.
What Is Bronchiolitis?
Bronchiolitis is a viral infection that targets the bronchioles, which are the smallest air passages in the lungs. The infection causes swelling and mucus buildup, restricting airflow and leading to breathing problems. It is most common in babies under two years old, particularly those younger than six months.
This illness spreads easily through coughing, sneezing, or close contact with infected individuals. Because young children have weaker immune systems, they are more vulnerable to catching it.
Common Causes of Bronchiolitis
The most frequent cause of bronchiolitis is the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), but other viruses can also trigger it. Some common causes include:
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)
- Influenza virus
- Rhinovirus
- Adenovirus
- Human metapneumovirus
Children who attend daycare or live in crowded environments have a higher risk of exposure.
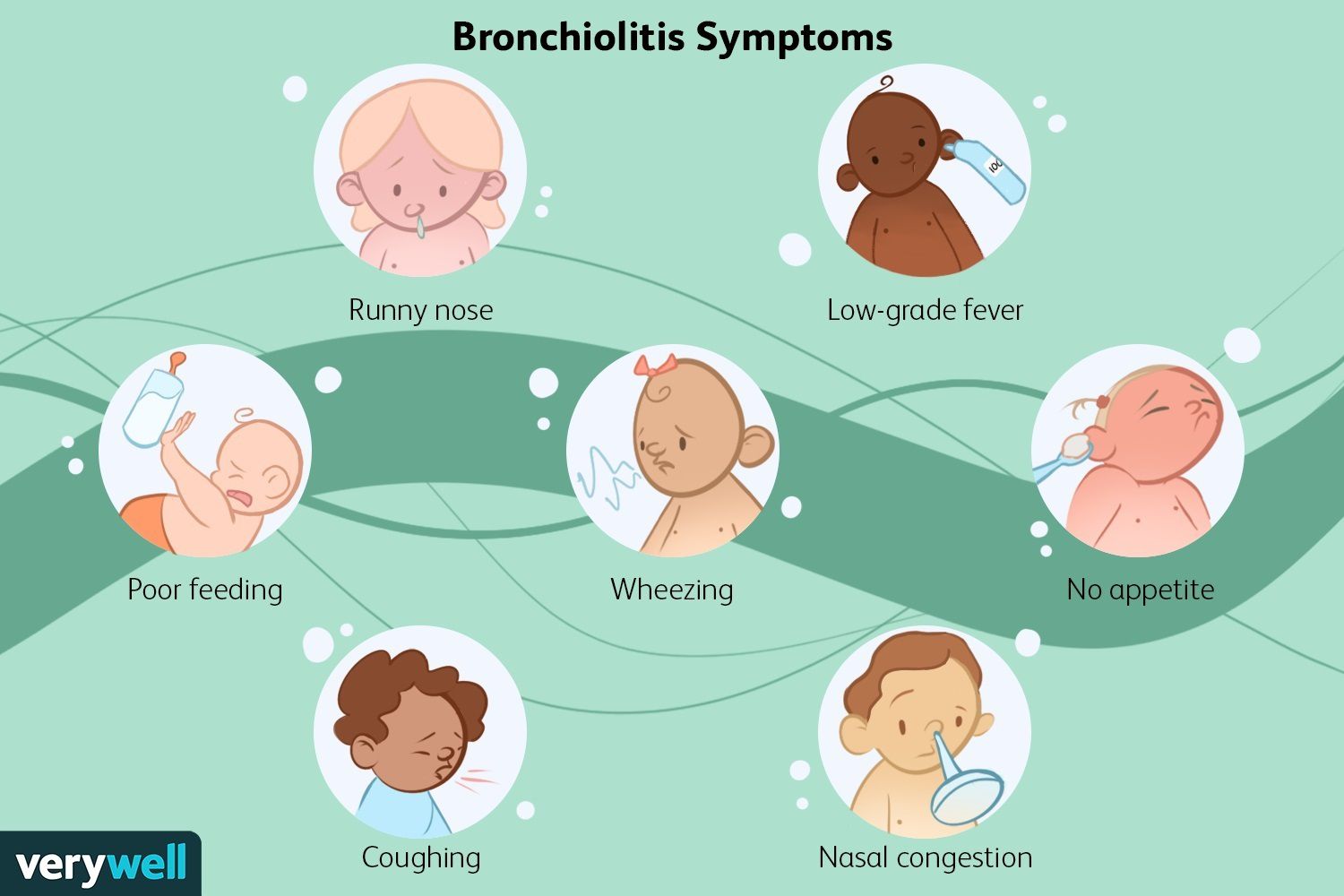
Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
Bronchiolitis symptoms usually start mild and worsen over time. Early symptoms resemble a common cold, but later signs can become serious.
Early Symptoms
- Runny nose
- Mild cough
- Fever
- Sneezing
Severe Symptoms
- Rapid or difficult breathing
- Wheezing sound while breathing
- Chest retractions (skin pulling in between ribs)
- Poor feeding
- Blue lips or fingertips
If any severe symptoms appear, immediate medical attention is required.
Who Is at Higher Risk?
Some children are more likely to develop severe bronchiolitis than others. High-risk groups include:
- Premature babies
- Infants under 6 months old
- Children with heart or lung conditions
- Babies exposed to secondhand smoke
- Children with weak immune systems
These children may require hospitalization for proper care.
How Doctors Diagnose Bronchiolitis
Doctors usually diagnose bronchiolitis through physical examination and medical history. They listen for wheezing sounds and check breathing patterns. In severe cases, additional tests may include:
- Chest X-ray
- Oxygen level monitoring
- Viral testing
Most cases do not require extensive testing unless symptoms are serious.
Treatment Options for Bronchiolitis
There is no specific cure for bronchiolitis because it is caused by viruses. Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms and supporting breathing.
Home Treatment for Mild Cases
- Keep the child hydrated
- Use saline nasal drops
- Maintain a humid environment
- Ensure proper rest
Hospital Treatment for Severe Cases
- Oxygen therapy
- IV fluids
- Suctioning mucus
- Breathing support
Antibiotics are not effective unless a bacterial infection is present.
How Long Does Bronchiolitis Last?
Most children recover within 7 to 14 days, although coughing may continue for several weeks. Recovery time depends on the child’s age, immune strength, and severity of infection.
Possible Complications
Although most cases are mild, bronchiolitis can lead to complications in severe situations, such as:
- Pneumonia
- Dehydration
- Respiratory failure
- Long-term breathing issues
Early treatment greatly reduces the risk of complications.
Prevention Tips for Parents
Preventing bronchiolitis is possible with proper hygiene and care. Some effective preventive measures include:
- Wash hands frequently
- Avoid close contact with sick individuals
- Keep babies away from crowded places
- Clean toys and surfaces regularly
- Avoid smoking near children
- Encourage breastfeeding for stronger immunity
Vaccines for certain viruses can also help reduce risk.
Difference Between Bronchiolitis and Bronchitis
Many people confuse bronchiolitis with bronchitis, but they are different conditions. Bronchiolitis affects small airways and mainly impacts infants, while bronchitis affects larger airways and is common in adults. Symptoms may appear similar, but treatment and severity differ significantly.
When to See a Doctor
You should seek medical help immediately if your child:
- Has trouble breathing
- Refuses to eat or drink
- Becomes unusually sleepy
- Turns blue around lips or face
Early medical intervention can save lives in severe cases.
Final Thoughts
Bronchiolitis is a serious yet common childhood illness that requires awareness and quick action. Recognizing symptoms early, providing proper care, and following preventive measures can help protect children from severe complications. With timely treatment and attention, most children recover fully and return to normal health.





